Treatments
#Male Infertility
Low sperm count, obstructions in the sperm transport system, aberrant sperm function, or erectile dysfunction are all factors that can lead to male infertility. Male infertility can be caused by illnesses, injuries, persistent health problems, and lifestyle choices. These might be secondary to chronic health issues such as Diabetes Mellitus, Obesity, internal organ damage, lifestyle decisions, or unknown reasons (accounts for a larger group). The inability to conceive a child can be stressful and disappointing, but male infertility can be treated in a variety of ways.

#Erectile Dysfunction
When a guy is unable to obtain or maintain a hard adequate erection for sexual intercourse, this condition occurs. Erectile dysfunction can be a symptom of a medical or mental ailment. It can lead to anxiety, relational conflict, and low self-esteem. Patients with erectile dysfunction should be checked for any underlying medical or psychological issues first.
#Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
The disorder polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) alters a woman’s hormone levels. PCOS causes women to create more male hormones than they should. This hormonal imbalance leads them to miss menstrual cycles, making it difficult for them to conceive. Hair growth on the face and body, as well as baldness, are all symptoms of PCOS.
PCOS is underdiagnosed and undertreated. This might be due to the fact that symptoms can be modest or appear to be unrelated. However, untreated PCOS can lead to a variety of more serious health problems, and the disorder’s symptoms can be quite distressing.
Type 2 diabetes, infertility, cardiovascular illness, obesity, sleep apnea (breathing problems while sleeping), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and depression are all linked to untreated PCOS. Early detection and treatment can dramatically lessen these risks. After a brief examination or a few simple tests, healthcare experts may usually confirm a diagnosis With These Tests.

PCOS and fertility
Ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovary) occurs once a month in persons who do not have PCOS.
People with PCOS may ovulate less regularly or consistently, making it difficult to plan intercourse during their menstruation cycle’s viable days when ovulation occurs. If ovulation occurs only every few months, it may take longer to become conceived.
These patients are also at a higher risk of miscarriage due to hormonal abnormalities.
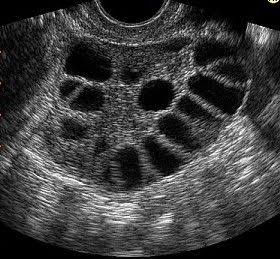
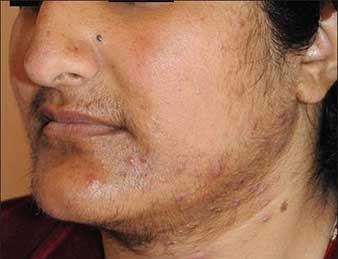

#Premature ovarian failure
When the ovaries cease working regularly as we get older, this is known as early menopause. When this happens, your ovaries don’t create enough oestrogen or release eggs on a regular basis. Infertility is a common side effect of this illness.
Symptoms :
Irregular or skipped periods, which might be present for years or develop after a pregnancy or after stopping birth control pills
Difficulty getting pregnant
Hot flashes
Night sweats
Vaginal dryness
Dry eyes
Irritability or difficulty concentrating
Decreased sexual desire
If you haven’t had your period in 3 months or more, check with your doctor to figure out what’s going on.
#Hormonal Imbalance
Hormones are the chemical messengers in your body. These potent substances are produced in the endocrine glands and circulate through your circulation, instructing tissues and organs on what to perform. They aid in the regulation of many of your body’s essential functions, such as metabolism and reproduction. You have too much or too little of a specific hormone when you have a hormonal imbalance. Even minor adjustments can have a significant impact on your entire body.
PCOD, thyroid problems, prolactin abnormalities, and other illnesses can cause hormonal imbalance.
Hormones play a crucial part in your general well-being. As a result, a wide range of signs and symptoms may indicate a hormonal imbalance. The indications and symptoms you experience will be determined by whatever hormones or glands are malfunctioning. Weight gain, unexplained and often unexpected weight loss, weariness, increased appetite, decreased sex desire, melancholy, nervousness, anxiety, or irritability, infertility, and other issues are all prevalent.
Signs or symptoms in Females
The polycystic ovarian syndrome is the most frequent hormonal abnormality in females of reproductive age (PCOS). Female-specific symptoms of a hormonal imbalance include:
Heavy or irregular periods, including missed periods, a stopped period, or a frequent period.
Hirsutism, or excessive hair on the face, chin, or other parts of the body.
Acne on the face, chest, or upper back.
Hair loss.
Vaginal dryness & vaginal atrophy.
Pain during sex.
Signs or symptoms in Males
Testosterone is an important factor in male development. If you don’t produce enough testosterone, it might cause a variety of symptoms. Hormonal imbalance can emerge in a variety of ways in adult guys.
Gynecomastia, or the development of breast tissue.
Erectile dysfunction (ED)
Decrease in beard growth and body hair growth.
loss of muscle mass, bone mass, otherwise known as osteoporosis.
Treatment options for a hormonal imbalance
The sort of hormonal imbalance will determine the treatment, which will be recommended by the doctor following an examination and medical study.
Estrogen therapy
Vaginal estrogen
Hormonal birth control
Anti-androgen medications
#Tubal Factor
The thin hollow tissue that links each ovary to the uterus is known as the fallopian tube. An egg is released from an ovary and travels through the fallopian tube to the uterus. Sperm will move upwards toward the egg if they are present in the uterus.
Fertilization takes occurs in the fallopian tubes most of the time. Cilia, a tiny hair-like substance inside the tubes, sweeps the embryo toward the uterus. It should then implant and develop for 9 months in the uterine lining.
When the fallopian tube(s) stops sperm from reaching the egg for fertilization or a fertilized egg (an embryo) from accessing the uterus for conception, tubal factor infertility develops.
A sperm and an egg cannot meet if the fallopian tube is damaged, deformed, or clogged in some manner, resulting in infertility. However, the injury to the tube may allow fertilization of the egg and sperm, but the embryo will be unable to move to the uterus and will remain in the tube.
The inability to conceive is the most common sign of tubal factor infertility. Many women are unaware that their fallopian tubes have been damaged until they visit a doctor for infertility.
Tubal infertility may also be present when infertility is accompanied by indications of pelvic inflammatory illness, such as persistent lower abdomen discomfort. A hysterosalpingogram, sonosalpingogram, and laparoscopy are utilized to identify tubal factors.
Surgical and non-surgical techniques to repair the damaged tube are the two major therapies for tubal factor infertility (s). In the event that these attempts fail, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is usually used to achieve pregnancy. If the doctor and the patient agree that IVF has the highest probability of success and is the best option for them, it may be used as the first therapy.



